-
- Trading Platforms
- PU Prime App
- MetaTrader 5
- MetaTrader 4
- PU Copy Trading
- Web Trader
- PU Social
-
- Trading Conditions
- Account Types
- Spreads, Costs & Swaps
- Deposits & Withdrawals
- Fee & Charges
- Trading Hours
In the ever-dynamic Forex market, where volatility reigns supreme, candlestick patterns serve as a powerful tool to anticipate price movements and guide trading decisions. Among these, the Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern stands out for its reliability in signalling potential bearish reversals. With its distinct structure and significant implications, the Shooting Star pattern acts as a red flag, indicating that bullish momentum may be waning and sellers could soon take control.
Rooted in the centuries-old art of Japanese candlestick charting, the Shooting Star pattern embodies the timeless principles of market psychology. Despite its historical origins, this pattern remains a cornerstone of modern technical analysis, valued for its simplicity and effectiveness in interpreting price behaviour.
Whether you’re just starting out or are a seasoned trader, mastering the Shooting Star can significantly enhance your ability to recognise and seize bearish market opportunities with confidence.
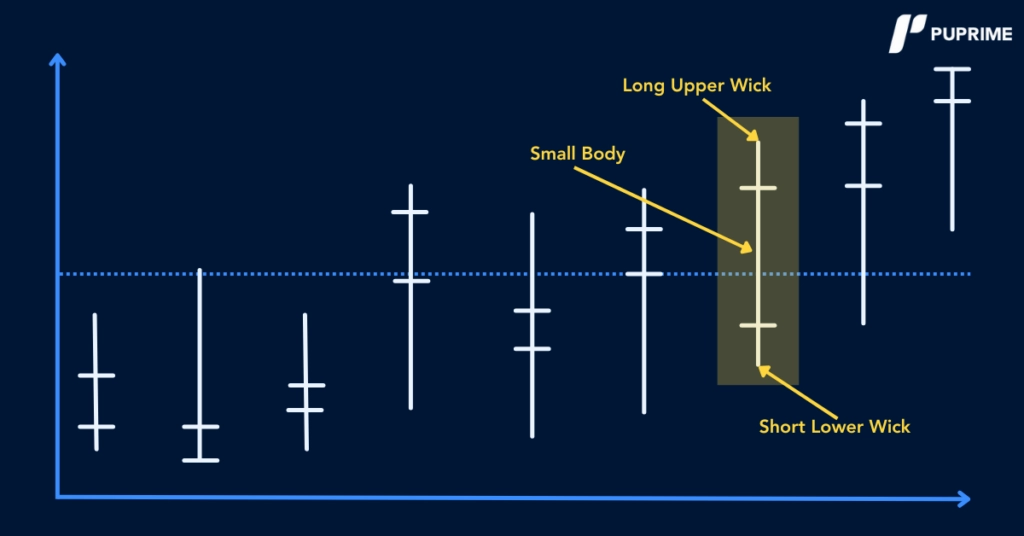
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a single-candle formation that emerges after an upward price trend, signalling a potential reversal. Its distinctive shape and positioning on the chart make it easily recognisable, even for novice traders seeking to identify shifts in market momentum.
In Forex trading, the Shooting Star is a valuable indicator of bearish reversals, particularly after strong upward trends in currency pairs.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a simple yet effective tool for identifying bearish reversals. By understanding its formation, structure, and market implications, traders can gain an edge in spotting potential turning points and making well-informed trading decisions.
Spotting a Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern requires careful observation of its unique features and understanding the market conditions in which it forms. While its distinct structure makes it easy to recognise, context is critical to ensure its effectiveness as a bearish reversal signal.
Modern trading platforms like PU Prime, TradingView and MetaTrader make identifying Shooting Star patterns easier and more efficient:
Identifying a Shooting Star involves more than recognising its structure—it requires placing it in the right context of an uptrend and seeking confirmation through volume and subsequent price action. By leveraging modern trading tools, traders can streamline this process and increase the accuracy of their trading decisions.
The Shooting Star Pattern reflects a critical shift in market psychology, marking a transition from bullish optimism to bearish control. Understanding the meaning behind this candlestick pattern provides valuable insights into trader behaviour and market sentiment, helping traders anticipate potential reversals.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern reveals the underlying psychology of market participants. By understanding its formation, context, and implications, traders can anticipate bearish reversals and adjust their strategies to align with the shifting market sentiment.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is predominantly a bearish reversal signal, appearing at the top of an uptrend. However, variations like the bullish Shooting Star (also referred to as the Inverted Hammer) exist, signalling potential reversals under specific conditions.
The Shooting Star Pattern is a widely recognised tool for identifying bearish reversals, but its reliability is not absolute. To use it effectively, traders must understand the factors that enhance or diminish its success.
The Shooting Star is a powerful bearish reversal pattern, but its reliability hinges on market context, volume confirmation, and follow-through price action. By combining it with resistance levels, technical indicators, and confirmation candles, traders can significantly improve its effectiveness. However, caution is essential to avoid false signals, and traders should always seek validation before executing trades.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a versatile tool that can be seamlessly integrated into trading strategies. Its effectiveness in signalling bearish reversals makes it a valuable asset for traders aiming to capitalise on short-term price movements or protect gains in existing long positions.
Steps to applying a Shooting Star-based strategy in Forex:
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern provides a framework for identifying bearish reversals and implementing strategic trades. By combining this pattern with technical indicators, clear entry and exit rules, and sound risk management, traders can enhance their ability to profit from market reversals while minimising potential losses.
The Shooting Star and Hanging Man candlestick patterns are visually distinct and serve different purposes in technical analysis. While both are single-candle patterns that often appear at the top of an uptrend, their context, structure, and implications differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for traders to apply each pattern effectively.
| Feature | Shooting Star | Hanging Man |
| Location | Top of an uptrend | Top of an uptrend |
| Wick Position | Long upper wick | Long lower wick |
| Sentiment | Bearish reversal | Potential reversal or indecision |
| Confirmation Needed | Important but less critical | Essential to validate bearish signal |
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a powerful tool for identifying bearish reversals, but its effectiveness depends on proper usage. Traders often make mistakes that undermine its reliability and lead to poor trading outcomes. By recognising and avoiding these pitfalls, traders can maximise the pattern’s potential and improve their success rates.
By waiting for confirmation, analysing market context and volume, managing risk, and correctly identifying patterns, traders can unlock the full potential of the Shooting Star as a reliable bearish reversal signal.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a cornerstone of technical analysis, prized for its ability to signal potential bearish reversals in trending markets. By mastering its structure, understanding the psychology behind it, and recognising its market implications, traders can effectively incorporate this pattern into their trading strategies.
Wait for Confirmation: Always look for the next candlestick to close below the Shooting Star’s low to validate the bearish signal and reduce the risk of false entries.
Combine with Technical Tools: Enhance the pattern’s reliability by pairing it with volume analysis, key resistance levels, and complementary indicators like RSI or Bollinger Bands.
Apply Disciplined Risk Management: Use stop-loss orders above the Shooting Star’s high and ensure proper position sizing to minimise losses and protect capital.
The Shooting Star’s simplicity and effectiveness make it a versatile tool for traders at all skill levels. By integrating this pattern into your trading approach, you can gain valuable insights into market sentiment and identify bearish opportunities with greater confidence.
To refine your skills, practise spotting and applying the Shooting Star in a demo account with PU Prime. With time and experience, you’ll be better equipped to leverage this powerful pattern in live market conditions.
Otherwise, when you are ready, step into the world of trading with confidence today. Open a free PU Prime live trading account today to experience real-time market action.
Step into the world of trading with confidence today. Open a free PU Prime live CFD trading account now to experience real-time market action, or refine your strategies risk-free with our demo account.
This content is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without considering any individual investment objectives, financial situations. Any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or investment product are not indicative of future results.
PU Prime makes no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of this content and accepts no liability for any loss or damage arising from reliance on the information provided. Trading involves risk, and you should carefully consider your investment objectives and risk tolerance before making any trading decisions. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.

Trade forex, indices, metal, and more at industry-low spreads and lightning-fast execution.
Sign up for a PU Prime Live Account with our hassle-free process.
Effortlessly fund your account with a wide range of channels and accepted currencies.
Access hundreds of instruments under market-leading trading conditions.
Please note the Website is intended for individuals residing in jurisdictions where accessing the Website is permitted by law.
Please note that PU Prime and its affiliated entities are neither established nor operating in your home jurisdiction.
By clicking the "Acknowledge" button, you confirm that you are entering this website solely based on your initiative and not as a result of any specific marketing outreach. You wish to obtain information from this website which is provided on reverse solicitation in accordance with the laws of your home jurisdiction.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!
Ten en cuenta que el sitio web está destinado a personas que residen en jurisdicciones donde el acceso al sitio web está permitido por la ley.
Ten en cuenta que PU Prime y sus entidades afiliadas no están establecidas ni operan en tu jurisdicción de origen.
Al hacer clic en el botón "Aceptar", confirmas que estás ingresando a este sitio web por tu propia iniciativa y no como resultado de ningún esfuerzo de marketing específico. Deseas obtener información de este sitio web que se proporciona mediante solicitud inversa de acuerdo con las leyes de tu jurisdicción de origen.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!

In the ever-dynamic Forex market, where volatility reigns supreme, candlestick patterns serve as a powerful tool to anticipate price movements and guide trading decisions. Among these, the Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern stands out for its reliability in signalling potential bearish reversals. With its distinct structure and significant implications, the Shooting Star pattern acts as a red flag, indicating that bullish momentum may be waning and sellers could soon take control.
Rooted in the centuries-old art of Japanese candlestick charting, the Shooting Star pattern embodies the timeless principles of market psychology. Despite its historical origins, this pattern remains a cornerstone of modern technical analysis, valued for its simplicity and effectiveness in interpreting price behaviour.
Whether you’re just starting out or are a seasoned trader, mastering the Shooting Star can significantly enhance your ability to recognise and seize bearish market opportunities with confidence.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a single-candle formation that emerges after an upward price trend, signalling a potential reversal. Its distinctive shape and positioning on the chart make it easily recognisable, even for novice traders seeking to identify shifts in market momentum.

In Forex trading, the Shooting Star is a valuable indicator of bearish reversals, particularly after strong upward trends in currency pairs.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a simple yet effective tool for identifying bearish reversals. By understanding its formation, structure, and market implications, traders can gain an edge in spotting potential turning points and making well-informed trading decisions.
Spotting a Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern requires careful observation of its unique features and understanding the market conditions in which it forms. While its distinct structure makes it easy to recognise, context is critical to ensure its effectiveness as a bearish reversal signal.
Modern trading platforms like PU Prime, TradingView and MetaTrader make identifying Shooting Star patterns easier and more efficient:
Identifying a Shooting Star involves more than recognising its structure—it requires placing it in the right context of an uptrend and seeking confirmation through volume and subsequent price action. By leveraging modern trading tools, traders can streamline this process and increase the accuracy of their trading decisions.
The Shooting Star Pattern reflects a critical shift in market psychology, marking a transition from bullish optimism to bearish control. Understanding the meaning behind this candlestick pattern provides valuable insights into trader behaviour and market sentiment, helping traders anticipate potential reversals.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern reveals the underlying psychology of market participants. By understanding its formation, context, and implications, traders can anticipate bearish reversals and adjust their strategies to align with the shifting market sentiment.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is predominantly a bearish reversal signal, appearing at the top of an uptrend. However, variations like the bullish Shooting Star (also referred to as the Inverted Hammer) exist, signalling potential reversals under specific conditions.
The Shooting Star Pattern is a widely recognised tool for identifying bearish reversals, but its reliability is not absolute. To use it effectively, traders must understand the factors that enhance or diminish its success.
The Shooting Star is a powerful bearish reversal pattern, but its reliability hinges on market context, volume confirmation, and follow-through price action. By combining it with resistance levels, technical indicators, and confirmation candles, traders can significantly improve its effectiveness. However, caution is essential to avoid false signals, and traders should always seek validation before executing trades.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a versatile tool that can be seamlessly integrated into trading strategies. Its effectiveness in signalling bearish reversals makes it a valuable asset for traders aiming to capitalise on short-term price movements or protect gains in existing long positions.
Steps to applying a Shooting Star-based strategy in Forex:
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern provides a framework for identifying bearish reversals and implementing strategic trades. By combining this pattern with technical indicators, clear entry and exit rules, and sound risk management, traders can enhance their ability to profit from market reversals while minimising potential losses.
The Shooting Star and Hanging Man candlestick patterns are visually distinct and serve different purposes in technical analysis. While both are single-candle patterns that often appear at the top of an uptrend, their context, structure, and implications differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for traders to apply each pattern effectively.
| Feature | Shooting Star | Hanging Man |
| Location | Top of an uptrend | Top of an uptrend |
| Wick Position | Long upper wick | Long lower wick |
| Sentiment | Bearish reversal | Potential reversal or indecision |
| Confirmation Needed | Important but less critical | Essential to validate bearish signal |
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a powerful tool for identifying bearish reversals, but its effectiveness depends on proper usage. Traders often make mistakes that undermine its reliability and lead to poor trading outcomes. By recognising and avoiding these pitfalls, traders can maximise the pattern’s potential and improve their success rates.
By waiting for confirmation, analysing market context and volume, managing risk, and correctly identifying patterns, traders can unlock the full potential of the Shooting Star as a reliable bearish reversal signal.
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern is a cornerstone of technical analysis, prized for its ability to signal potential bearish reversals in trending markets. By mastering its structure, understanding the psychology behind it, and recognising its market implications, traders can effectively incorporate this pattern into their trading strategies.
Wait for Confirmation: Always look for the next candlestick to close below the Shooting Star’s low to validate the bearish signal and reduce the risk of false entries.
Combine with Technical Tools: Enhance the pattern’s reliability by pairing it with volume analysis, key resistance levels, and complementary indicators like RSI or Bollinger Bands.
Apply Disciplined Risk Management: Use stop-loss orders above the Shooting Star’s high and ensure proper position sizing to minimise losses and protect capital.
The Shooting Star’s simplicity and effectiveness make it a versatile tool for traders at all skill levels. By integrating this pattern into your trading approach, you can gain valuable insights into market sentiment and identify bearish opportunities with greater confidence.
To refine your skills, practise spotting and applying the Shooting Star in a demo account with PU Prime. With time and experience, you’ll be better equipped to leverage this powerful pattern in live market conditions.
Otherwise, when you are ready, step into the world of trading with confidence today. Open a free PU Prime live trading account today to experience real-time market action.

Trade forex, indices, metal, and more at industry-low spreads and lightning-fast execution.
Sign up for a PU Prime Live Account with our hassle-free process.
Effortlessly fund your account with a wide range of channels and accepted currencies.
Access hundreds of instruments under market-leading trading conditions.
Sign up for a PU Prime Live Account with our hassle-free process.
Effortlessly fund your account with a wide range of channels and accepted currencies.
Access hundreds of instruments under market-leading trading conditions.